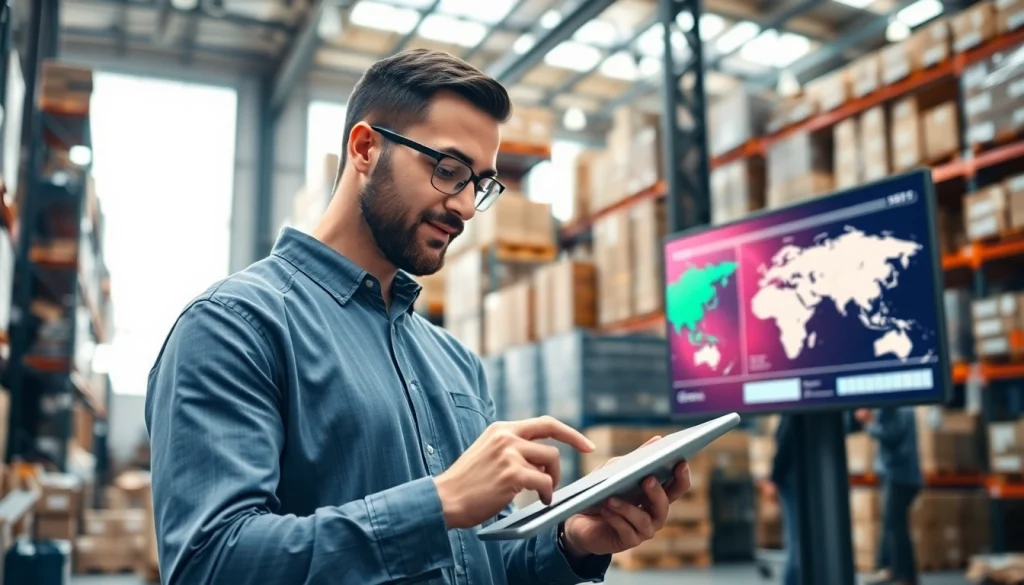
What is Logistics?
Definition and Scope of Logistics
Logistics is a dynamic field that deals with the efficient forward and reverse flow of goods, services, and related information from the point of origin to the point of consumption. It integrates various functions within supply chain management, focusing on the movement, storage, and management of resources and products. The scope of logistics encompasses transportation, warehousing, inventory management, order fulfillment, and more, all aimed at maximizing customer satisfaction while minimizing costs.
In essence, logistics serves as the backbone of both domestic and international trade, facilitating the seamless movement of products across geographical boundaries.
Types of Logistics: An Overview
Logistics can be categorized into various types based on different criteria. The primary types include:
- Inbound Logistics: Focuses on the transportation and storage of incoming goods from suppliers to the manufacturing unit.
- Outbound Logistics: Deals with the distribution of finished products from the manufacturing site to the end consumer.
- Third-Party Logistics (3PL): Involves outsourcing logistics operations to external companies that specialize in providing logistics services.
- Military Logistics: Pertains to the planning and execution of logistics in a military context, ensuring that armed forces have the necessary supplies and equipment.
- Integrated Logistics Support: A comprehensive approach that encompasses all aspects of logistics, ensuring system reliability over its lifecycle.
The Importance of Logistics in Supply Chain Management
The role of logistics in supply chain management is critical. It serves as a strategic function that ensures the smooth operation of supply chains by coordinating various processes, including procurement, inventory management, and transportation. Effective logistics management helps businesses:
- Enhance customer service by ensuring timely and accurate deliveries.
- Reduce operational costs through optimized shipping and warehousing.
- Improve inventory management by balancing supply with demand.
- Facilitate better communication between suppliers, manufacturers, and customers.
In a competitive marketplace, the importance of logistics cannot be overstated, as it influences not just cost savings but also customer satisfaction and overall business efficiency.
Key Components of Logistics
Transportation Management
Transportation management is a core component of logistics, responsible for planning, executing, and optimizing the movement of goods. This involves selecting the right transportation modes, such as road, rail, air, or sea, to ensure timely deliveries while minimizing costs. Key elements of effective transportation management include:
- Route Optimization: Utilizing software solutions and data analytics to determine the most efficient routes for delivery.
- Carrier Selection: Choosing carriers based on cost, reliability, and service quality, ensuring that they align with business objectives.
- Real-Time Tracking: Implementing tracking systems that provide visibility into the status of shipments, enabling proactive communication with customers.
Warehousing and Storage Solutions
Warehousing plays a vital role in logistics, acting as the intermediary between production and distribution. Efficient warehousing solutions are crucial for managing inventory levels, minimizing costs, and ensuring timely deliveries. Key aspects include:
- Inventory Management: Utilizing advanced inventory management systems to track stock levels and prevent overstock or stockouts.
- Warehouse Layout Optimization: Designing warehouse layouts for efficient movement of goods and improved picking accuracy.
- Value-Added Services: Offering packaging, assembly, or kitting services within warehouses to enhance customer offerings.
Inventory and Order Management
Effective inventory and order management are crucial for maintaining the balance between supply and demand. This entails managing stock levels, forecasting demand, and ensuring timely order fulfillment. Best practices include:
- Just-in-Time Inventory: Reducing inventory holding costs by receiving goods only when needed for production or sales.
- Demand Forecasting: Using historical data and market analysis to anticipate future demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly.
- Automated Order Processing: Implementing technology to automate order entry and processing, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
Challenges in Logistics Management
Common Logistics Obstacles
Logistics management faces several challenges that can impact overall efficiency and effectiveness. Common obstacles include:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Natural disasters, geopolitical issues, and pandemics can disrupt supply chains, causing delays and increasing costs.
- Rising Transportation Costs: Fluctuations in fuel prices and transportation capacity can significantly impact logistics costs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to regulations and standards across different geographic locations can complicate logistics operations.
Impact of Technology on Logistics Challenges
Technology has revolutionized logistics, but it also presents challenges. While it offers solutions for improving efficiency, it can create complexity. Key impacts include:
- Data Management: The exponential growth of data can overwhelm logistics providers who lack robust data management systems.
- Integration Issues: Integrating new technologies with existing logistics systems can pose challenges, leading to inefficiencies.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Increased reliance on technology heightens the risk of cyberattacks, potentially disrupting operations.
Strategies to Overcome Logistics Barriers
Addressing logistics challenges requires strategic planning and implementation. Effective strategies include:
- Adopting Technology: Leveraging automation, artificial intelligence, and IoT (Internet of Things) to streamline operations and enhance visibility.
- Building Resilient Supply Chains: Diversifying suppliers and creating contingency plans to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
- Continuous Training and Development: Ensuring workforce training on the latest technologies and best practices to adapt to industry changes.
Best Practices for Successful Logistics Operations
Leveraging Technology for Efficient Logistics
Incorporating cutting-edge technology into logistics operations is essential for achieving efficiency. Best practices include:
- Implementing Transportation Management Systems (TMS): Utilizing TMS can enhance decision-making and streamline transportation processes.
- Adopting Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): WMS can improve inventory accuracy, order fulfillment speed, and overall warehouse efficiency.
- Utilizing Data Analytics: Analyzing data can lead to insights that drive better logistics planning and performance.
Communication and Coordination in Logistics
Effective communication and coordination are vital for successful logistics operations. Best practices include:
- Establishing Clear Communication Channels: Ensuring that all stakeholders have access to the necessary information and updates.
- Collaborating with Suppliers and Customers: Fostering strong relationships with partners to ensure alignment and optimize processes.
- Regular Assessment of Performance: Conducting periodic reviews of logistics performance to identify areas for improvement.
Continuous Improvement in Logistics Processes
To stay competitive in the logistics industry, organizations must embrace continuous improvement methodologies. Key aspects include:
- Implementing Lean Principles: Focusing on waste reduction and efficiency can improve logistics processes and reduce costs.
- Engaging Employees in Change Initiatives: Encouraging employee feedback can lead to innovative solutions and enhance operational efficiency.
- Benchmarking Against Industry Standards: Comparing performance metrics against industry standards can reveal areas needing attention.
Measuring Logistics Performance
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Logistics
Establishing KPIs is crucial for evaluating logistics performance. Common KPIs include:
- On-Time Delivery Rate: Measures the percentage of orders delivered on or before the promised date.
- Order Accuracy: Examines the accuracy of orders shipped compared to orders placed.
- Transport Cost per Unit: Assesses transportation costs relative to the number of units shipped, helping to identify inefficiencies.
Tools and Techniques for Performance Measurement
Various tools and methods can be employed to track logistics performance effectively:
- Dashboards: Real-time dashboards provide insights into logistics metrics and simplify performance tracking.
- Surveys and Feedback Tools: Gathering customer feedback can provide insights into service quality and areas for improvement.
- A/B Testing: Experimenting with different logistics strategies can help identify the most efficient methods.
Using Metrics to Drive Logistics Efficiency
Metrics should not just be compiled; they need to inform strategic decisions. Some approaches include:
- Conducting Root Cause Analysis: Investigating the underlying causes of performance issues can lead to actionable solutions.
- Setting Benchmarks: Creating performance benchmarks enables organizations to gauge their logistics effectiveness relative to competitors.
- Aligning Metrics With Strategic Goals: Ensuring that KPIs align with broader organizational goals increases their relevance and impact.